Akari is conducting a pre-clinical research program to develop long-acting PAS-nomacopan with the potential for three key benefits: complement inhibition, fewer doses, and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) inhibition to address the risks of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) associated complement-only inhibitors approved for GA treatment.

References
1. Liao DS, et al., Complement C3 inhibitor pegcetacoplan for geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration – a randomised phase 2 trial. Opthalmology 2019; 127: 586-195.
2. Jaffe GJ, et al., C5 inhibitor avacincaptad peg for geographic atrophy due to age-related macular degeneration – a randomised pivotal phase 2/3 trial. Ophthalmology 2021; 128: 576-586.
3. McClard CK, et al. Questionnaire to Assess Life Impact of Treatment by Intravitreal Injections (QUALITII): Development of a patient-reported measure to assess treatment burden of repeat intravitreal injections. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2021;6(1):e000669.
4. Sasaki F, et al., Leukotriene B4 promotes neovascularisation and macrophage recruitment in murine wet-type AMD models. JCI Insight 2018; 3: e96902.
1. Complement C5 inhibition to slow GA progression
Efficacy of complement C3 and C5 inhibition in slowing progression of GA lesions is well understood1,2
2. Fewer needle injections into the eye
Frequent need injections into the back of the eye are a source of fear, discomfort, and disruption for patients3; potential for 4 or fewer injections with PAS-nomacopan each year
3. LTB4 inhibition may reduce risk of CNV
LTB4 inhibition may prevent VEGF-A overexpression, a key driver of sight-threatening CNV,4 a safety risk (treated with VEGF inhibitors) associated with complement-only inhibitors approved for GA treatment
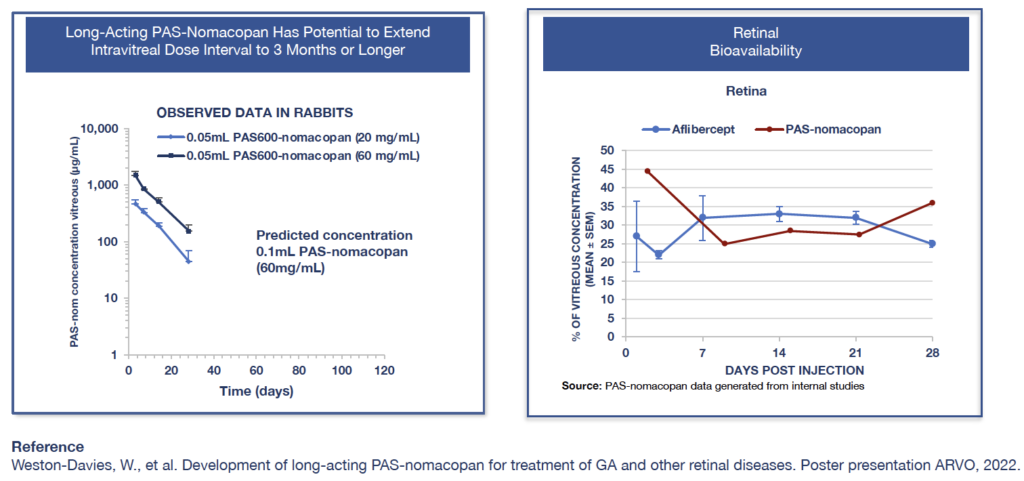
Long-acting PAS-nomacopan has the potential for 4 or fewer injections into the eye per year. PK/PD data show PAS-nomacopan has extended half-life in the eye after intravitreal injection (7.4 to 8.4 days), suggesting the dose interval may be 3 months or longer.
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV), a sight-threatening condition associated with complement-only inhibitors approved for GA treatment, is driven by overexpression of the VEGF-A protein. Because LTB4 can activate overexpression of VEGF-A, PAS-nomacopan LTB4 inhibition may help to prevent CNV.
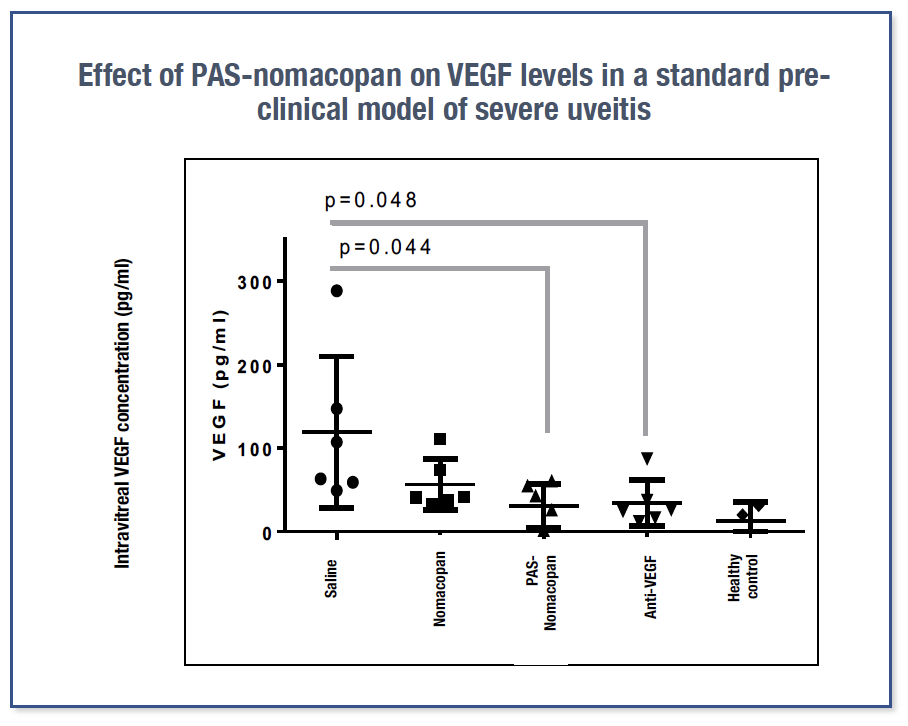
In a pre-clinical model of severe uveitis, long-acting PAS-nomacopan (single IVI) decreased VEGF levels (VEGF-A is a key driver of CNV) as effectively as anti-VEGF antibody treatment 1,2.
LTB4 promotes laser induced CNV in a pre-clinical model of wet age-related macular degeneration3.
References
Eskandarpour M, et al., Leukotriene B4 and its receptor in experimental autoimmune uveitis and in human retinal tissues – clinical severity and LTB4 dependence of retinal Th17 cells. Am J Pathol. 2021; 191:320-334
Eskandapour M, et al., Immune mediated retinal vasculitis in posterior uveitis and experimental models: the leukotriene (LT)B4-VEGF axis. Cells 2021; 10:396
Sasaki F, et al., Leukotriene B4 promotes neovascularization and macrophage recruitment inn murine wet-type AMD models. JCI Insight 2018; 3:e96902